Essential oils can be extracted and extracted from the leaves, flowers, peels, seeds, roots, bark, resin, etc. of plants through various physical and chemical extraction methods. Most of the essential oils are distilled, while most of the citrus essential oils are used. Prepared by cold pressing.
A simple classification of essential oil extraction methods
| Extraction method | classification | Get product |
| Distillation | Steam distillation 2. Steam distillation 3. Water and steam distillation |
Essential oil, pure dew |
| Cold pressing | Citrus | Essential oil, vegetable oil |
| Fat absorption | Flower | Pomade |
| Impregnation method | – | Soaking oil (belonging to vegetable oil) |
| Solvent extraction | Resin 2. Flowers and plants 3. Take the condensate for alcohol extraction |
Spice extract 2. Aroma 3. Original essence |
| Supercritical extraction | Carbon dioxide CO2 extraction | Essential oil |
Distillation
It is the most common method of extracting essential oils and is suitable for plants that are heat-resistant and will not be destroyed. There are three ways to do this:
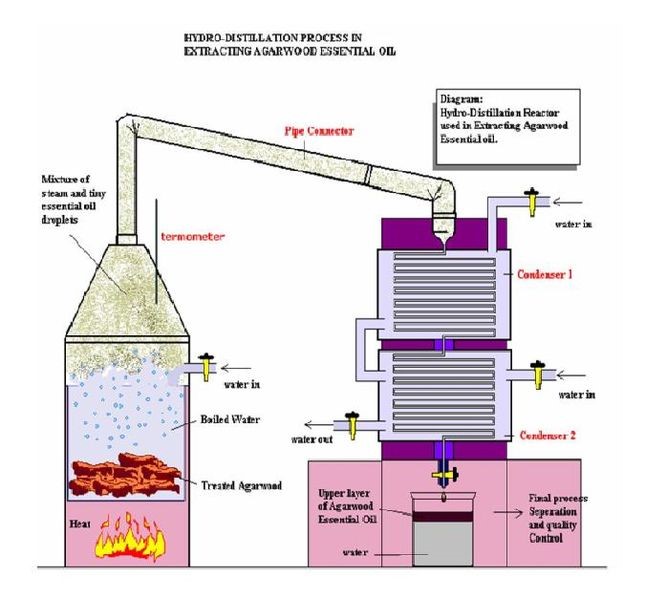
1. Water Distillation – Directly immerse the plant in water and boil it. This method is most commonly used to extract flower essential oils to prevent the flowers from gathering together during distillation, making it difficult to pass the vapor.
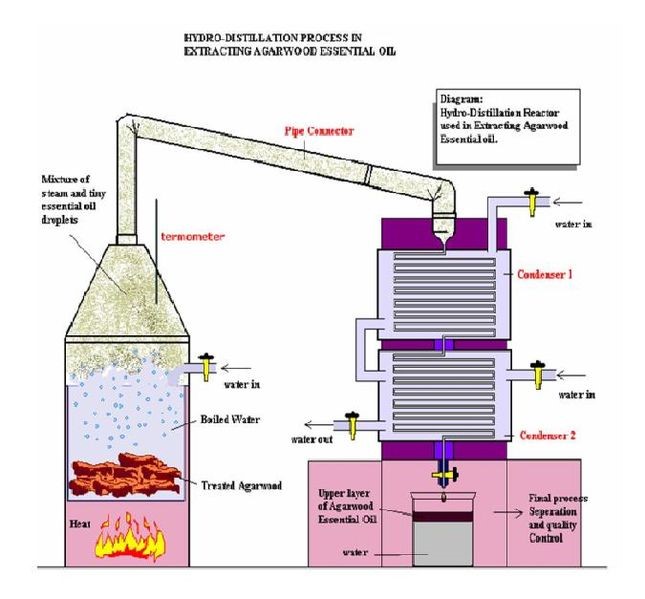
water distillation
2. Steam Distillation – In this process, the water is placed under the plants to heat, so that the water vapor is passed up through the plants, the essential oil is extracted, and the water vapor with the essential oil is condensed into a liquid through the conduit, and the specific gravity is transmitted. The difference can be separated into oil and water layers, the oil layer is the essential oil, and the water layer is pure dew (or water), which is the most commonly used distillation method.
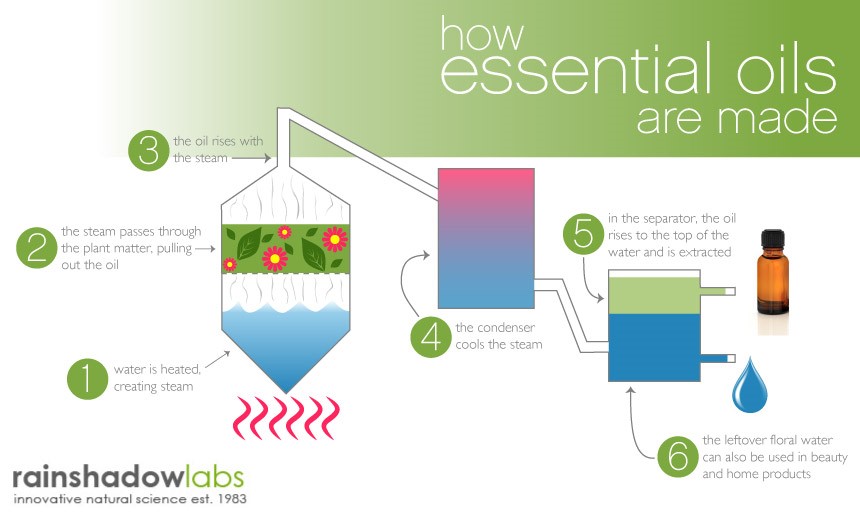
Steam Distillation
3. Water and Steam Distillation: The first two methods are used in combination with each other.
Cold-pressed / Press method (Expression)
The cold pressing method is applied to citrus essential oils or base oils, by pressing the peel or pulp, adding water to the juice, and finally separating the essential oil from the juice (water layer) by centrifugal force. For example sweet orange, grapefruit, orange, lemon, lime oil and so on.
It is worth noting that cold pressing means not a low-temperature environment, but a lower operating temperature (40-60 ° C) than a typical high-temperature extraction.
Fat absorption method (Enfleurage)
This method is very old and traditional and has disappeared from the market. Apply grease (tallow or lard) to the glass frame, then spread the petals on top, use the grease to absorb the essence, and constantly change the petals until the oil absorbs the saturation, and then extract and separate with alcohol. The process takes several weeks or more. It is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and costly, so it does not meet economic value.

Enfleurage1
The product obtained in this way, called Pomade, can be said to be a very outdated product. Taiwan does not even have a unified translation. Strictly speaking, Pomade can no longer be called essential oil. Compared with the current essential oil products, the concentration is much lower. Today, apart from the French perfume capital – Grasse, a few extraction plants, which are extracted by fat extraction for tourists, are generally extinct for commercial use.
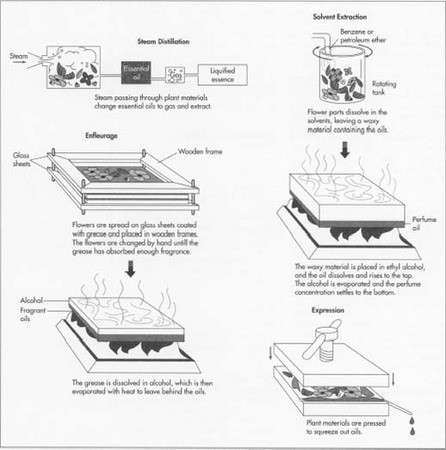
Enfleurage2
Dipping method (Maceration) / soaking method/oil bubble method
Soak the aromatic plants in hot oil (usually vegetable oil) to break the oil cells of the plant, and the hot oil will absorb the released essence, and finally filter and purify. The oil obtained by the impregnation method, referred to as infused oils (Infused Oils or Macerated Oils), is generally classified in vegetable oils, such as calendula oil, carrot oil, St. John’s wort oil, Leigong root oil, arnica oil, and the like.

Maceration
Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction in a broad sense, in addition to chemical solvents, such as: ether, hexane, toluene, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, alcohol, etc., even including carbon dioxide (CO2), animal oil, vegetable oil, etc., using the solvent to dissolve the plant The essence of the extract is extracted; since the boiling point of the chemical solvent is much lower than that of the essential oil, the vacuum distillation method (in the low pressure environment, the boiling point of the solvent can be lowered to prevent the essential oil molecules from being destroyed), the chemical solvent is separated.

Solvent Extraction
Usually, after the first solvent extraction (usually with petroleum ether or hexane), the concentration of the effective substance obtained is extremely high, and after removing the solvent, a wax is obtained, which is called a flavor extract or a fragrance. It contains a lot of wax, pigment pigments and aromatic substances. After taking the second solvate extraction (alcohol), the obtained product is the original essence.
Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
The supercritical extraction method is a solvent extraction method in which a supercritical fluid (SCF) is used as solvent extraction, and an extract (for example, an essential oil) is extracted from a matrix (an aromatic plant), which is also one of solvent extraction methods. Currently used in the food industry (such as degreasing, decaffeination, etc.), the pharmaceutical industry (vitamin separation and refining) and the cosmetics industry (ie, essential oil extraction).
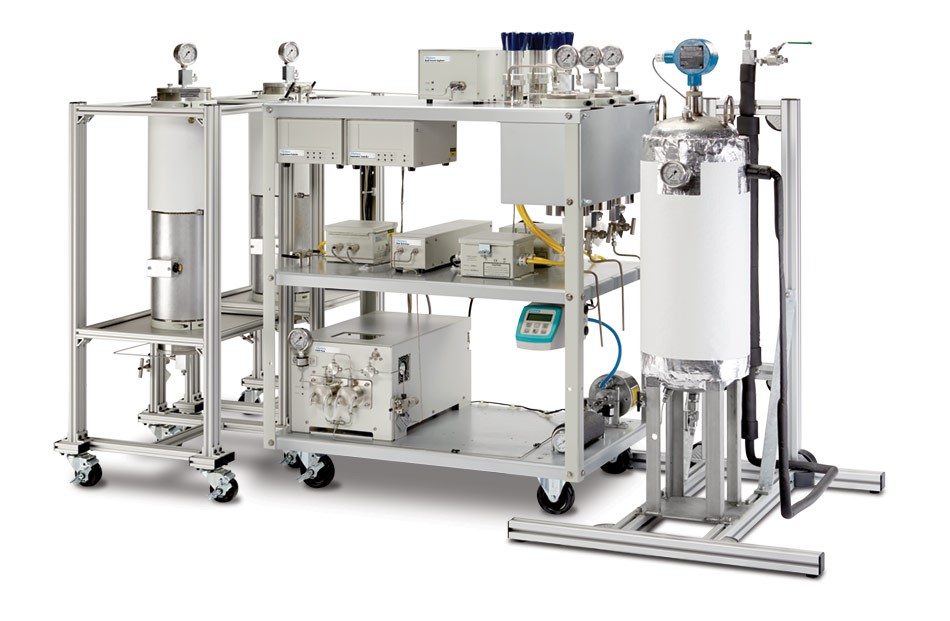

Supercritical
The most commonly used supercritical fluid is carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), which is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, non-combustible, non-reactive to most substances, and low in gas cost; compared to common distillation and solvent extraction methods, Low temperature, no solvent residue and so on.
Common carbon dioxide extraction essential oils include ginger, frankincense, and calendula essential oils. Due to the rich composition, the odor is different from the general distillation extraction.